A box-type substation is a prefabricated, compact electrical equipment that assembles high-voltage switchgear, distribution transformers and low-voltage electrical devices according to a certain wiring method. With the development of the economy and the acceleration of the urbanization process, such box-type substations have the characteristics of strong complete set, small size, compact structure, safe and reliable operation, convenient maintenance, low investment, quick effect, and short power transmission cycle. It is widely used in urban and rural power grids. Especially due to various factors such as urban planning and rapid land appreciation, small-capacity box-type substations (below 1,0008) have become the first choice for users with convenient installation and small footprint. know. As a result, the market demand has expanded year by year, and many electrical appliance manufacturers have been manufacturing, and various box-type substations have appeared in the market. The biggest feature of the box-type substation is: "Using a combination of standardized products to fully meet the power supply needs of specific users." Since it is specific, it is not universal, which requires the manufacturer to design and manufacture according to different user needs. There are differences in the capacity of the power supply transformer used by the user, the number of switch circuits, the peripheral environment, and the layout. Since the transformer is installed in the outdoor box, whether the heat generated by the outdoor sun and the transformer itself can be dissipated to ensure the normal operation of the transformer has become the most concerned issue for users. The following will focus on the temperature rise of box-type substations and discuss some of our company's experience and experience in the manufacturing process of box-type substations for everyone to discuss and jointly improve the manufacturing level of box-type substations in my country.
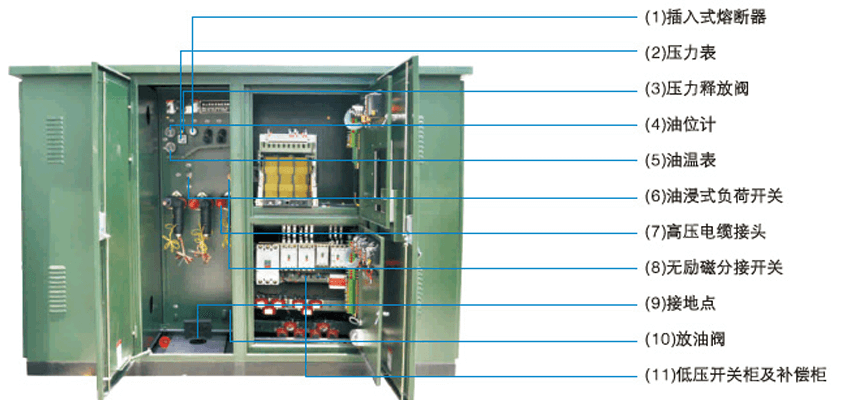
1、Temperature rise is the main limiting factor for the life and power of the box transformer
The main heating element of the box-type transformer, the transformer, will produce losses during operation, and these losses will all be converted into heat. Part of the heat increases the temperature of the transformer itself, and the other part is emitted to the surrounding air. All electromagnetic carriers of transformers are heating elements, and the core and winding are the main heating elements.
The life of a transformer depends on the life of its insulating medium. Under normal operating conditions, it is mainly the temperature that has an impact on the insulating medium. Long-term high temperature will cause the aging of the insulating medium and gradually lose its electrical resistance.
All kinds of insulating media have a certain life under the action of a certain temperature. The absolute materials used in oil-immersed transformers are mainly insulating paper and cardboard, and the design life is generally 20 years. Through testing and production practice, it is believed that the long-term allowable maximum temperature of the insulating medium corresponding to the 20-year lifespan is about 98°C. That is to say, the absolute image medium in the oil-immersed transformer can operate continuously for twenty years under the action of the temperature of 98℃.
The temperature of each part of the transformer is different. When operating under rated conditions, the temperature of each part should not exceed the maximum working temperature allowed by the insulating material. so,
The GB1094 standard stipulates that the normal operating conditions of oil-immersed transformers are:
The altitude does not exceed 1000m, the highest temperature is +40°C, the average temperature of the hottest month is +30°C, the highest annual average temperature is +20°C, etc. The temperature rise limit of the transformer in the steady state of continuous rated capacity is specified as: the top oil The temperature rise is 55K (non-fully sealed type), and the average temperature rise of the winding is 65K. The temperature rise limit specified in the standard is based on the annual average temperature of the air around the transformer of 20°C, which is the difference between the top oil temperature and the average winding temperature and the annual average air temperature of 2°C. The most important thing in the insulation of the transformer is the winding insulation. Generally speaking, the difference between the hottest spot temperature of the winding and the average temperature is 13K, so the average temperature rise limit of the winding is 98-20-1365K.
The heat generated by the transformer during operation is dissipated by three research forms: heat conduction, heat radiation and time flow. From the winding to the winding surface, the heat is dissipated by heat conduction; from the winding surface to the oil, it is dissipated by convection; the heat is dissipated from the outer wall of the oil tank to the air by convection and radiation. . The temperature difference between the outer wall of the oil tank and the air is the largest, accounting for about 60% to 70% of the total temperature rise. From this point of view, the ambient temperature of the transformer operation is very important.
Now dry-type transformers are installed in many box-type substations. The winding temperature rise limit of dry-type transformers is 100K, and the difference between the hottest spot temperature and the average temperature is 15K. The normal operating conditions of dry-type transformers are the same as oil transformers. However, the dry-type transformer is a much higher heat source than the oil, and there is a large temperature gradient from the dry-type transformer to the space inside the substation and then to the space outside the substation. General dry-type transformers are equipped with fans and fans, which can be operated under forced air cooling. The fans make the temperature of the transformer dissipate to the surrounding medium faster. This requires box-type substations to have better ventilation and heat dissipation conditions. The temperature inside and outside the substation is required to remain unchanged to achieve this, but the temperature rise of the substation to the outside air must be controlled to minimize it.

















